Photodetector Basics SAMPLE
Photodiodes are electronic components that are used to detect light and convert it into an electrical signal. They are widely used in various applications such as cameras, optical communication systems, and medical equipment. In this blog post, we will provide an introductory explanation of the mechanism of photodiodes to help you get acquainted with this important electronic component.
The basic principle behind the operation of a photodiode is the photoelectric effect. This effect was first discovered by Albert Einstein in 1905 and explains how photons (particles of light) can knock electrons out of atoms or molecules when they strike them. When a photon strikes a semiconductor material such as silicon or germanium, it can create an electron-hole pair. The electron is free to move around in the material while the hole is a vacancy where an electron is missing.
In a photodiode, there are two regions: the p-type region and the n-type region. The p-type region has an excess of positively charged holes while the n-type region has an excess of negatively charged electrons. When light strikes the photodiode, it creates electron-hole pairs in both regions. The electrons and holes then move towards each other due to their opposite charges and create a current flow.
The amount of current generated by a photodiode depends on several factors such as the intensity of light, wavelength of light, and temperature. Photodiodes can be designed to detect different wavelengths of light by choosing appropriate semiconductor materials.
One important parameter that characterizes photodiodes is their responsivity, which is defined as the ratio of output current to incident optical power. Responsivity depends on several factors such as quantum efficiency (the probability that a photon will generate an electron-hole pair), absorption coefficient (the rate at which photons are absorbed), and collection efficiency (the probability that generated carriers will contribute to photocurrent).
In summary, photodiodes are electronic components that convert light into electrical signals based on the photoelectric effect. They are widely used in various applications and their performance depends on several factors such as responsivity, quantum efficiency, absorption coefficient, and collection efficiency.
Reference:
“Photodiode Amplifiers: OP AMP Solutions” by Jerald G. Graeme
“Optoelectronics: An Introduction” by John Wilson and John Hawkes
“Semiconductor Optoelectronic Devices: Introduction to Physics and Simulation” by Joachim Piprek

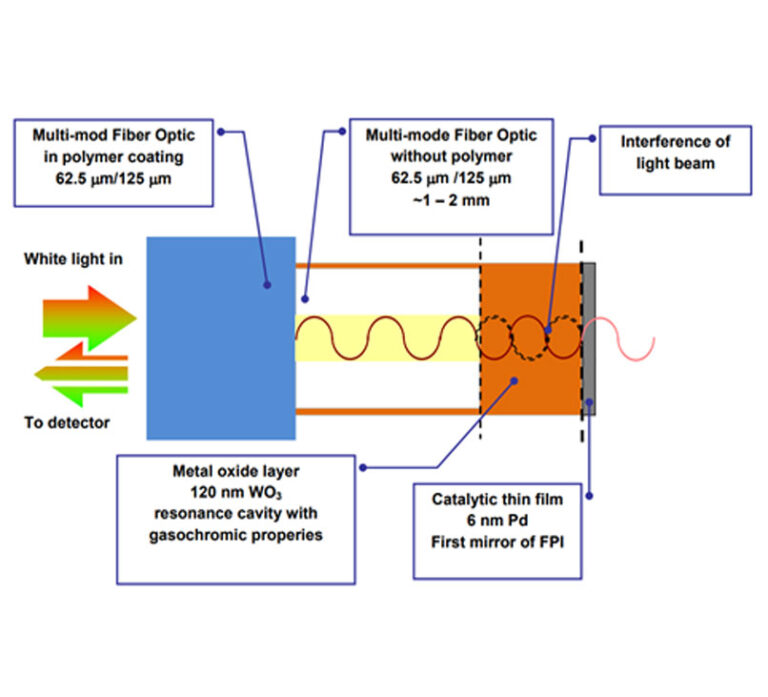
InnoWell is an innovative company in the field of the optical gateway and fiber-optics-based sensors. The various products of InnoWell can fulfill customers’ requirements for measuring temperature, and types of gasses, whether they are toxic or explosive in oil wells, besides identifying gas kick before occurrence.
Copyright © 2023 InnoWell. All Rights Reserved